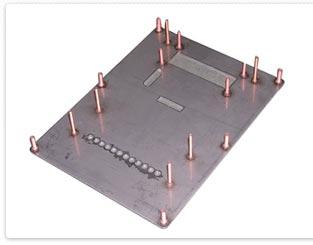
What is Stud Welding?
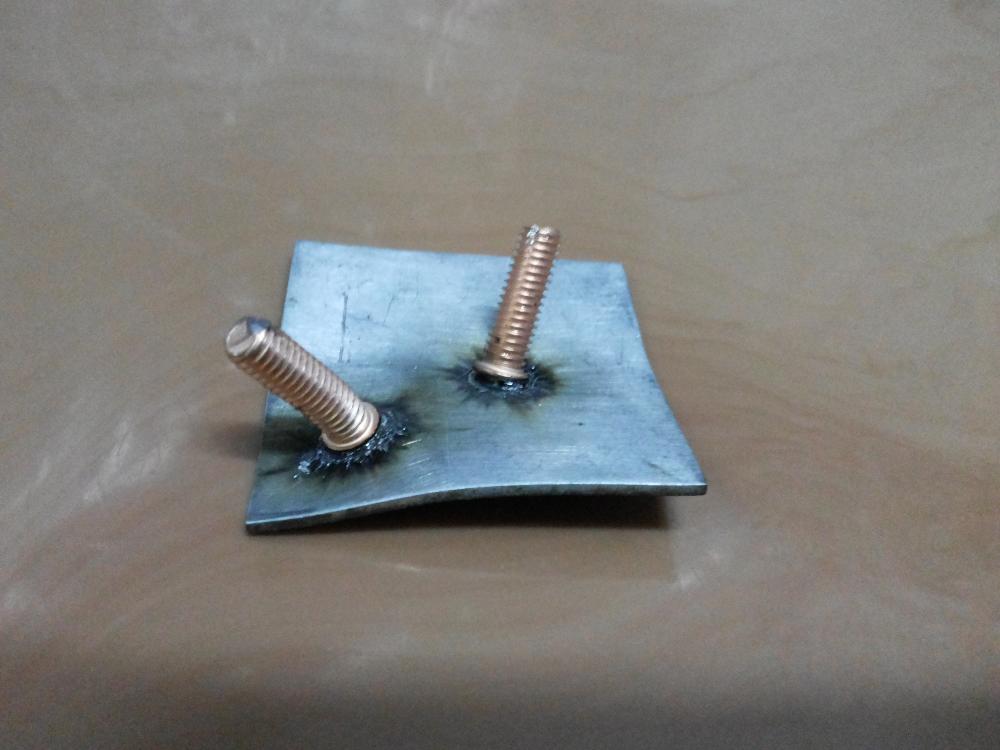
STUD WELDING is a high-speed metal fastening process in which a metal fastener can be applied by a welding arc to another piece of metal.
THE PROCESS OF STUD WELDING: The welding stud is placed (with a hand tool called the Stud Gun) in contact with the base metal, a weld arc is drawn which melts the welding stud base and an area of the metal work piece for metal fastening. The welding stud is then forced into the melted area and held in place until the metals re-solidify. This high quality fusion arc weld is complete in milliseconds and is accomplished by one of two major methods.
Stud Welding Applications
Stud Welding Applications:
- Electrical
- Electronic
- Mechanical
- Heating & Ventilation
- Decorative & Consumer
Typical Industries:
- Light Industries & Machine Construction
- Automotive & Switchgear Industries
- Fabricators & Cabinets
- Electrical & panel Industries
- Elevator & Cookware Industries
.png)
.png)



.png_t.jpg)
.png_t.jpg)

Advantages of Stud Welding
In many industries where metal is used Studwelding is providing fixing and fastening solutions.
- Fast attachment.
- No reverse marking.
- The welded joint is stronger than the parent material or the stud.
- Access is only required from one side.
- No holes hence no leaking or weakening of the sheet.
- Tamper proof.
- Pre-coated or painted material can be welded
Replacing Inserts
Stud welding replaced inserts in these applications, resulting in faster productions and stronger joints. Thinner sheets could now be used, and with no reverse marking.
Corrosion was eliminated as moisture ingress was prevented.
Replacing Drilling and Tapping
Studwelding allowed this manufacturer to speed up production considerably.
Previously he had to leak test every through drilled and tapped hole. An alternative solution of using thicker flanges would have resulted in additional time and cost implications
Replacing Back Welding
Here production increased tenfold when stud welding replaced a back welding process. With no need to grind the top surface flat and polish off excess material and burn marks, time saved was significant – reject components were eliminated with additional cost saving.
Replacing Through Bolting
One component became tamper-proof, a clean design was the biggest benefit on another. One a third part, the gauge was reduced and leakage was prevented. Finally stud welding solved the problem of loose bolts and inaccessibility to the bolt head after assembly.
Replacing Resistance Welding
Removed a bottleneck by not having to take the biggest component to a large resistance welding machine. Replacing soldering cured a corrosion problem caused by a solder flux. Some components which were previously brazed sustained damage because of the long heat cycle – stud welding eradicated this.
Stud welding Improves Design:
Stud welding provides an “invisible” fixing for fascia panels, counter tops, signs and badges – for any surface where final appearance, security or hygiene is paramount.
As stud welding does not break through the surface, there is no subsequent risks of leaks or corrosion on, for example, inspection hatches and cover plates; when mounting heating elements or attaching fluid chambers.
Stud welding in ideal for applications where access cannot be made to the reverse side of an assembly, such as mounting circuit boards, rails, instruments, earth points and many different components.
Stud welding is suitable for fixing fluid and air lines, wiring looms, machine guards, handles, insulations and fireproofing materials.




